Introduction
Switching to an electric vehicle is a significant milestone for Australian drivers. Yet the home charging setup that follows is just as important as the car itself. In Australia, the vast majority of EV charging happens at home, so getting the installation right isn’t just a convenience – it’s a safety and reliability issue. This guide walks you through what to expect when you install a home EV charger, including the steps, costs, and regulatory requirements, with practical tips to keep the process smooth and compliant.
Step-by-step breakdown of the installation process
While a licensed professional should handle the actual installation, understanding the journey helps you prepare and make informed decisions.
1) Initial site assessment
- A licensed electrician visits your home to assess: the age and condition of your switchboard, remaining capacity, and whether an upgrade is required to handle an additional charger circuit.
- They determine your home’s power supply type (single-phase vs three-phase) and how this affects charging speed at the wallbox (typical speeds: around 7.2 kW on single-phase; up to 22 kW on three-phase).
- The best charger location is identified, usually in a garage or carport, with safety and proximity to the switchboard in mind.
- Cable run distance from the switchboard to the proposed charger is measured, as this directly influences material and labour costs.
2) Quoting and product selection
- Based on the site assessment, you’ll receive a transparent quote covering:
- Labour: the electrician’s time and expertise.
- Materials: the charger unit, cabling, circuit breakers, and other hardware.
- Additional works: upgrades such as a new circuit, switchboard modifications, or trenching for outdoor installs.
- Your electrician can help you pick a charger that matches your needs (power rating, smart features, compatibility with home energy management).
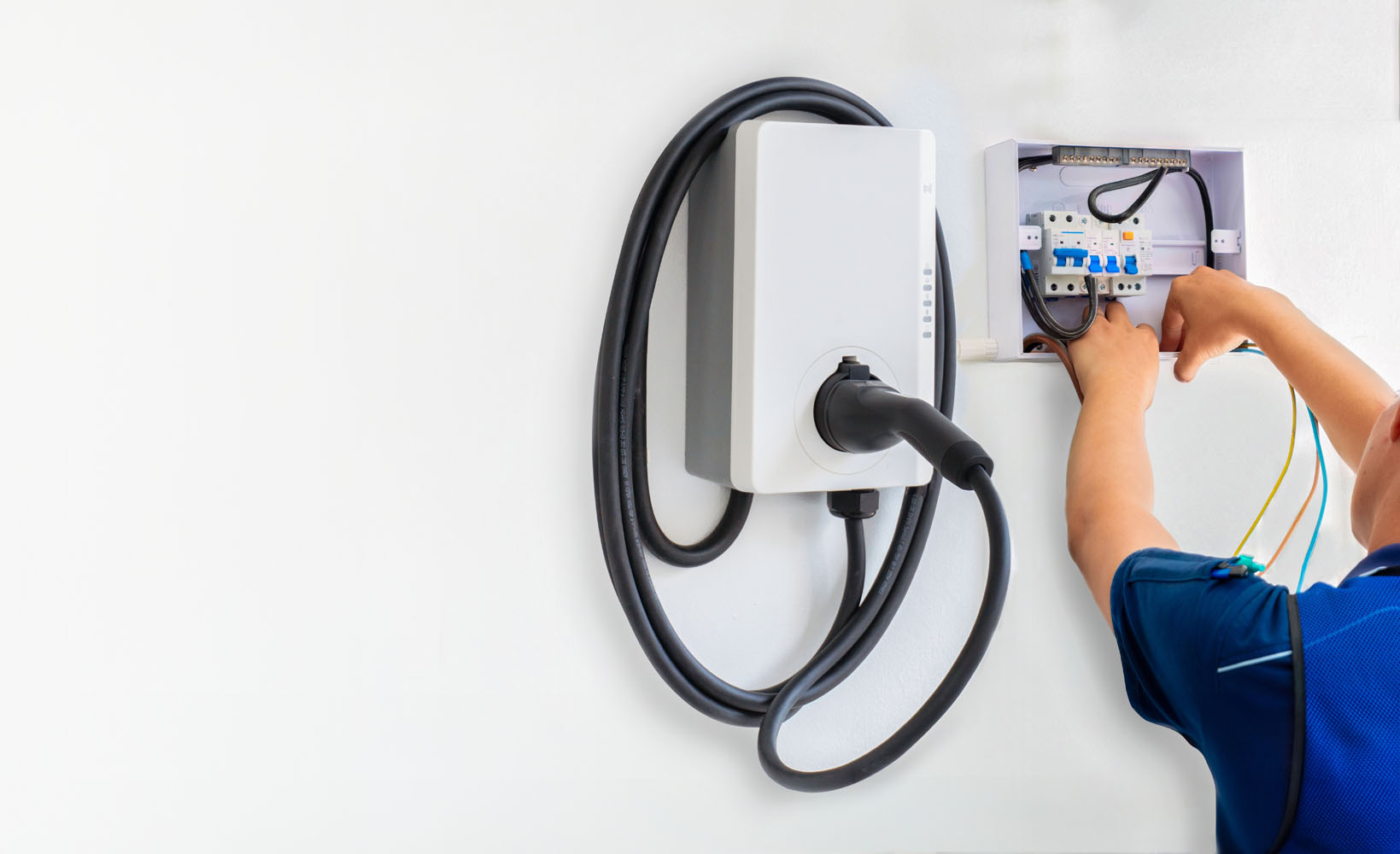
3) The installation
- Dedicated circuit: Australian regulations (AS/NZS 3000:2018) require the EV charger to be on its own dedicated circuit to prevent overloading and interference with other appliances.
- Safety devices: installation of an individual circuit breaker and a Residual Current Device (RCD) for the charger’s circuit protects against overcurrents and electric shock.
- Mounting and wiring: the wallbox is securely mounted to a wall or pedestal, with correctly sized cable run from the switchboard to the charger. Cables are protected from mechanical damage and installed to meet standards.
- Commissioning: post-install tests verify correct operation and safety. For smart chargers, the setup often includes configuring the app and enabling features like remote monitoring and load balancing.
4) Final checks and handover
- The electrician will confirm the system’s performance, provide basic usage guidance, and address any questions about future upgrades or maintenance.
Why a licensed electrician is non-negotiable
In Australia, fixed electrical installations, including EV chargers, must be performed by a fully qualified, licensed electrician. This is not merely a suggestion-it’s a legal requirement under the Australian and New Zealand Wiring Rules (AS/NZS 3000:2018). The rationale is clear:
- Safety: EV chargers draw continuous high current, so incorrect sizing or poor workmanship can lead to overheating, cable damage, short circuits, or fire risk.
- Compliance: A licensed professional certifies that the installation complies with national standards and local regulations.
- Warranty and insurance: Many charger manufacturers and home insurers require certified installation. An unlicensed job could void warranties and leave you exposed to significant costs if something goes wrong.
The cost of a home EV charger installation
Costs vary based on charger specs, home configuration, and location. Here’s a practical breakdown to help you budget.
- EV charger unit: $700 to $2,000+.
- Single-phase (about 7.2 kW): typically cheaper.
- Three-phase (11 kW or 22 kW): higher price due to increased power handling and equipment.
- Smart features: Wi‑Fi connectivity, solar integration, and load balancing add to the cost.
- Labour and materials: roughly $500 to $2,000 for a standard install.
- Standard installation: modern switchboard, garage location, shorter cable run.
- Complex installation: long cable runs, concrete drilling, or outdoor trenching can push costs higher.
- Potential upgrades (variable):
- Switchboard upgrade: $500 to $3,000+ if space is insufficient or the board is aged.
- Three-phase power upgrade: a more involved project that can cost several thousand dollars.
- Typical total range: $1,200 to $3,500 for a standard home charger installation, including the unit and installation. More involved projects can exceed this range.
Location, safety, and common issues to avoid
Choosing the right location is as important as the hardware you select.
- Ideal locations:
- Garage or carport: protected from the elements and convenient for regular charging.
- Outdoor installations: require an outdoor-rated unit with a high IP rating (IP44 or higher) and appropriate weatherproofing.
- Proximity considerations:
- Place the charger near your car’s charging port and in a spot that minimises cable length and tripping hazards.
- A site survey helps determine the best route for cabling to the switchboard.
- Common issues and how to avoid them:
- Circuit breaker tripping: usually a sign of an overloaded circuit or improper installation. A dedicated circuit with appropriate load management mitigates this risk.
- Slower-than-expected charging: may indicate an undersized cable, suboptimal switchboard capacity, or limited home power supply (single-phase vs three-phase). Confirm your electrical setup before purchasing a high-powered charger.
- Connectivity problems: for smart chargers, ensure a strong Wi‑Fi signal at the installation site; otherwise, features like remote monitoring may be unreliable.
Practical tips for a smoother install
- Plan for future needs: if you anticipate upgrading your EV or adding solar, discuss load management and solar-ready options with your electrician.
- Consider load management: some smart chargers balance charging with household energy use to maximise efficiency and avoid peak-rate charges.
- Outdoor readiness: for exterior installs, ensure the unit is rated for outdoor use and that the installation enclosure meets local weatherproofing standards.
Compliance, incentives, and ongoing maintenance
- Regulatory compliance: stay informed about any changes to wiring rules and local regulations that could affect future upgrades or inspections.
- Incentives and rebates: state and local incentives vary. Some programs support energy efficiency or solar-linked charging; check current government schemes and speak with your installer about eligible options.
- Maintenance: a once-and-done installation should be complemented by periodic checks, especially after major electrical work elsewhere in the home, to ensure continued safety and performance.
Conclusion
A well-planned home EV charger installation in Australia is a blend of safety, regulatory compliance, and practical efficiency. Engaging a licensed electrician from the outset ensures your system is correctly sized, safely wired, and compatible with your home’s electrical characteristics. With the right charger choice, smart features, and proper installation, you’ll unlock reliable home charging that supports your EV lifestyle for years to come.
FAQs
Do I really need a dedicated circuit for my EV charger?
Yes. Australian standards require the charger to be on its own dedicated circuit to prevent overloading and to safeguard the rest of your electrical system.
Can I install an EV charger myself to save money?
No. Fixed electrical work should be performed by a licensed electrician. DIY installation could be dangerous, violate regulations, void warranties, and affect insurance.
How long does installation typically take?
A standard installation usually spans a day or two, depending on site access and whether upgrades (switchboard or cable routing) are required. Complex jobs may take longer.
Will the charger affect my home insurance or warranty?
Potentially. Many insurers and charger manufacturers require certified installation. Confirm coverage with your insurer and read the warranty terms.
Should I choose single-phase or three-phase power for my home charger?
It depends on your home supply and charging needs. Single-phase chargers are common and adequate for many households, but three-phase options offer faster charging if your supply supports it.
What should I consider when selecting a charger?
Consider power output (kW), smart features (app control, scheduling, load management), compatibility with your EV, future energy plans (solar), and installation compatibility with your home’s electrical system.
How can I prepare for the site assessment?
Have documentation of your electrical panel, existing circuits, and any plans for home upgrades ready. Note the location of your EV parking spot and any preferences for charger placement.
Are there energy-saving or solar-integrated charging options?
Yes. Some chargers support solar integration and load balancing to maximise self-consumption and minimise grid draw, which can be cost-effective over time.
What about outdoor installations and weather considerations?
Choose an outdoor-rated unit (IP44 or higher) and ensure the installation complies with weatherproofing and cable protection standards.
Can incentives reduce the overall cost?
Some state or local programs offer incentives or rebates for EV charging or energy efficiency measures. Check current schemes in your state and consult your installer about eligibility.
About EV Evolution
EV Evolution is the leading online platform dedicated to Australian electric vehicle owners and enthusiasts. We foster a vibrant community, delivering essential EV news and insights, and enhancing user engagement through our innovative, AI-powered chatbot for dynamic discussions. Our mission is to empower Australian electric vehicle owners and enthusiasts by fostering a vibrant, AI-driven online community that connects, informs, and advances the nation’s electric vehicle landscape: EV Charger Installation in Australia: A Comprehensive Guide.